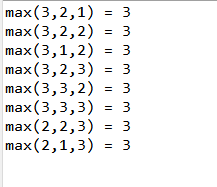알고리즘 입문(자바) - 01_1 알고리즘이란?
시간이 비교적 여유로울 때 알고리즘 공부를 하면 좋을 듯 싶어서,
회사에서 남는 시간에 알고리즘 공부를 하기로 했다.
사실 저번에 동영상을 보면서 공부했었는데 그것보단 책이 좋을 것 같으므로
책을 구입했다.
참고서적은 Do it! 자료구조와 함께 배우는 알고리즘 입문 : 자바 편
알고리즘이란?
-
알고리즘 알고리즘이란?
문제를 해결하기 위한 것으로, 명확하게 정의되고 순서가 있는 유한 개의 규칙으로 이루어진 집합 -
세 값의 최댓값
3개의 정숫값 가운데 ‘최댓값’을 구하는 프로그램.public class Example1 { public void max3() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Scanner stdIn = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("세 정수의 최댓값을 구합니다."); System.out.print("a의 값 : "); int a = stdIn.nextInt(); System.out.print("b의 값 : "); int b = stdIn.nextInt(); System.out.print("c의 값 : "); int c = stdIn.nextInt(); //a,b,c의 최댓값을 구하여 max에 대입 int max=a; if(b > max) max = b; if(c > max) max = c; System.out.println("최댓값은 " + max + " 입니다."); } }실행결과는 이렇다
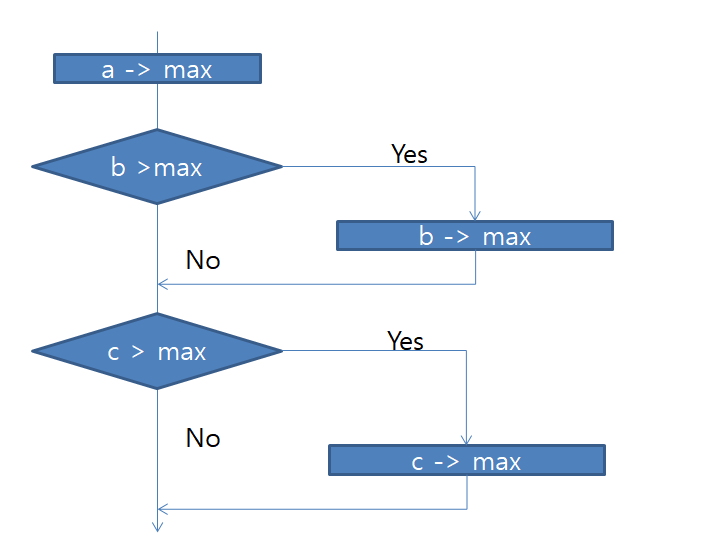
a, b, c의 최댓값을 구하는 과정은 다음과 같다.- max에 값을 넣는다.
- b값이 max보다 크면 max에 b를 넣는다.
- c값이 max보다 크면 max에 c를 넣는다.
세 문장이 나란히 있다면 순서대로 실행되다.
이렇게 여러 문장이 순차적으로 실행되는 구조를 순차적 구조라고 한다.
if문과 같이 프로그램 실행흐름을 변경하는 문을 선택구조라고 한다.
다음 순서도(flow chart)를 보면 더 이해가 쉽다.
- 여러 값에 대한 최댓값
public static void main(String[] args) { Example1 ex1 = new Example1(); System.out.println("max(3,2,1) = " + ex1.max3_1(3,2,1)); System.out.println("max(3,2,2) = " + ex1.max3_1(3,2,2)); System.out.println("max(3,1,2) = " + ex1.max3_1(3,1,2)); System.out.println("max(3,2,3) = " + ex1.max3_1(3,2,3)); System.out.println("max(3,3,2) = " + ex1.max3_1(3,3,2)); System.out.println("max(3,3,3) = " + ex1.max3_1(3,3,3)); System.out.println("max(2,2,3) = " + ex1.max3_1(2,2,3)); System.out.println("max(2,1,3) = " + ex1.max3_1(2,1,3)); } public int max3_1(int a, int b, int c) { int max = a; if(b > max) { max = b; } if(c > max) { max = c; } return max; }실행결과
보는 것과 같이 a, b, c를 순서나 중복 상관없이 다 다르게 입력해도
최댓값은 3으로 나오는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
- 세 값의 중앙값
public int Median(){ Scanner stdIn = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("a의 값 : "); int a = stdIn.nextInt(); System.out.print("b의 값 : "); int b = stdIn.nextInt(); System.out.print("c의 값 : "); int c = stdIn.nextInt(); if(a >= b ) { if(b >= c) { return b; }else if(a <= c) { return a; }else { return c; } }else if(a > c) { return a; }else if (b > c) { return c; }else { return b; } }실행결과
- 조건판단과 분기
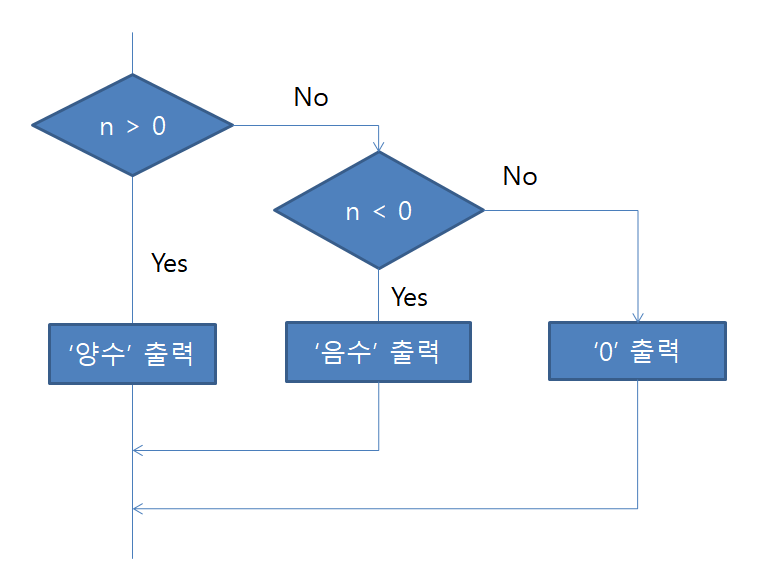
public void jubgeSign(){ Scanner stdIn = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("정수를 입력하세요 : "); int n = stdIn.nextInt(); if(n > 0) { System.out.println("이 수는 양수입니다."); }else if(n < 0) { System.out.println("이 수는 음수입니다."); }else { System.out.println("이 수는 0입니다."); } }실행결과
이 내용을 순서도로 나타내게 되면 아래와 같다.
위 코드의 경우에는 모든 상황에 맞는 코드가 된다.
아래처럼 고쳐보자!public void jubgeSign_1(){ Scanner stdIn = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("정수를 입력하세요 : "); int n = stdIn.nextInt(); if(n == 1) { System.out.println("이 수는 1입니다."); }else if(n == 2) { System.out.println("이 수는 2입니다."); }else if(n==3){ System.out.println("이 수는 3입니다."); } }실행결과
4를 입력하면 아무값도 출력되지 않는다.
그러나 이 코드에서 마지막 if 문의 조건만 고친다면 결과는 달라진다.public void jubgeSign_2(){ Scanner stdIn = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("정수를 입력하세요 : "); int n = stdIn.nextInt(); if(n == 1) { System.out.println("이 수는 1입니다."); }else if(n == 2) { System.out.println("이 수는 2입니다."); }else{ System.out.println("이 수는 3입니다."); } }실행결과
왜냐하면 ‘judgeSign_1’의 코드는 바로 아래 형식처럼 작동하기 때문이다.public void jubgeSign(){ Scanner stdIn = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("정수를 입력하세요 : "); int n = stdIn.nextInt(); if(n == 1) { System.out.println("이 수는 1입니다."); }else if(n == 2) { System.out.println("이 수는 2입니다."); }else if(n==3){ System.out.println("이 수는 3입니다."); }else { //공백문(실제로 아무것도 하지 않는 문장) } }